No products
Prices do not include tax.
Temperature control in the medical, pharmaceutical and chemical industries
Temperature monitoring in the medical, pharmaceutical and chemical industries is critical to comply with safety protocols. These healthcare sectors work with elements that are sensitive to temperature changes. In some cases, controlling the temperature in their environment is key to ensuring their proper performance.
Indicator labels are a practical resource we can use to control the temperature quickly and easily. Their heat-sensitive elements react to heat by changing colour and display the temperature, making it easier to monitor.Types of Medical & Pharmaceutical industries
- Transporting medicines and vaccines
Air transport of medicines
The transport of medicines at controlled temperatures requires the use of transport means with a cold chamber to prevent the cold chain of the medicines from being broken. In general, the temperature should always be kept between 2 °C and 8 °C. It is also essential to use a clean cold room, and carefully load the products to prevent breakage or similar accidents. That being said, controlling the cold chain is fundamental. This can be done using devices like temperature recorders or using simpler solutions, like adhesive indicators, which alert you by changing colour if there is a fault in the refrigeration, both due to excess or lack of cold.
What happens if a vaccine’s cold chain breaks?
The cold chain of thermolabile medicines must be maintained constantly to avoid altering their properties. If this happens, it increases the chance of biological contamination, and they become a serious health threat since their toxicity levels rise.
At first glance, it is impossible to detect whether the cold chain for vaccines has been broken. This makes it essential to have a temperature indicator that can warn us if the required thermal conditions were altered along the journey.Characteristics of proper transport of vaccines
For the transport of vaccines, we must also have vehicles with cold chambers, isothermal boxes, portable refrigerators, ice packs and, most of all, temperature control systems that ensure the preservation of the drugs’ cold chain.
When the cargo arrives at its destination, it must be placed in a vaccine refrigerator that is at the same temperature. The cold chain for vaccine preservation ensures the thermal stability of vaccines, thus minimizing the possibility of germ propagation or drug deterioration, which could create a health problem for the patient.
As we can see, professionals in the sector do not transport all medicines as if they were a single commodity. Following a strict protocol, they follow the laboratory’s instructions at all times to use the most appropriate transport. The temperature range is from 0 °C for vaccines to 25 °C for other commonly-used drugs that do not require refrigeration but do require temperature control.In these tasks, using irreversible temperature indicators allows unassisted control during transport. By permanently changing colour, they will alert you if the cold chain was broken at any point.
Traditional adhesive thermometers are also useful to check the temperature of the vaccine refrigerator and to prevent inadequate cooling in good time.
We believe we have covered the most important aspects of the transport of refrigerated medicines, thus helping you understand the importance of finding a carrier that strictly complies with the protocols, and uses a suitable temperature control method to ensure the proper preservation, as well as the durability and usability of each medicine. - Sterilization of surgical material
Sterilization of surgical material
Here we have three options: dry heat, autoclave and chemicals. As we will see below, however, only two of them are the most used nowadays.
Dry heat
It is carried out using Poupinel ovens, which can heat the instruments to 180 °C.The downside is that you have to wait for them to cool down before using them and that such a high temperature causes them to deteriorate prematurely. It is the least used method.
Autoclave
It consists of two chambers: one external and one internal, in which steam is used to eliminate germs. The most used is the so-called pre-vacuum autoclave. Inside, the oxygen is vacuumed and the steam enters at a temperature of 121-134 °C. Then the vacuum is created once again, and finally, the cooling stage takes place.
Chemicals
Options such as ethylene oxide, formaldehyde, plasma gas and hydrogen peroxide are arranged in chambers for the immersion of the corresponding surgical material.
Sterilization of laboratory equipment
Also, those explained in the following sections must be added to those mentioned above.
Dry heat autoclave
The aim is for the proteins to be denatured, the lipids to melt, and the microorganisms to be dewatered. It is quite a mildly aggressive method for metal instruments. It is suitable for the sterilization of viscous or powdery substances and is effective at a temperature of 120 °C.
Radiation
Radiation is ionizing, given its effectiveness in easily eliminating microorganisms. Gamma radiation is often chosen because of its ability to penetrate. It is very effective in removing germs from Petri dishes.
Sterilization methods used in microbiology laboratories
Two broad groups can be distinguished, including some of the options already outlined.
Chemicals
Alcohols (isopropyl and ethanols), aldehydes (glutaraldehyde and formaldehyde), phenols (xylenol and carbolic acid), ethylene oxide and hydrogen peroxide are mainly used.
Physical methods
Autoclave, dry heat, hot air, incineration, tyndallization, pasteurization, boiling and steam, among others.
We hope that we have given you the necessary facts to know how the sterilization of surgical material and laboratory material works.
Medical & Pharmaceutical industries Best seller
LCD reversible adhesive temperature indicator. This label changes colour on the basis of the temperature.
Reversible temperature indicator for the...44,49 €Tempsafe is an adhesive label changing colour by any temperature increase and displaying a message to alert on hot surfaces and avoid burns.
Tempsafe safety temperature indicator...32,49 €The TDI adhesive temperature label is an indicator coming with three irreversible temperature points. It has been specifically manufactured to control the sanitizing of industrial dishwashers.
TDI Label- TDI Thermometer for the control...314,27 €This product is supplied in packets with 10 thermometers. Irreversible-type temperature indicator with 8 temperature points. This is an adhesive thermometer than can be stuck on any surface or product. The points are marked with temperature in ºC and ºF.
8-level irreversible thermometers (pack 10...15,93 €Irreversible time and temperature indicator by color change. This adhesive label alerts you to inappropriate temperature exposure by progressively changing the color of the control points. Each point is calibrated for a specific period of time, thus allowing control of the exposure time at that temperature.
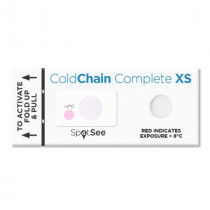
WarmMark Time and Temperature (pack 100...238,00 €Coldchain complete XS is a temperature label for cold chain control. This indicator is irreversible and alerts us by means of a color change if a product has been exposed outside the required temperature range, both above and below it. It is supplied in packs of 100 units.
Coldchain Complete XS cold chain...322,00 €
Uses of temperature monitoring in the medical industry
When making its devices, temperature is one of the factors that the medical industry takes into account. Although body thermometers are the most common, we can find more items that are used to precisely monitor degrees. One of these items are incubators where newborns complete their development and are kept at physiological limits of 36-37 °C.Processes for the sterilization of medical materials are another example. In these cases, specific heat levels are applied over a period of time. Some of these processes are sterilization through vapour to kill germs or dry heat used mainly for glass and other laboratory materials. And, of course, worth mentioning is the need for temperature control in hospitals and healthcare centres.
Maintaining the temperature in the pharmaceutical industry
Maintaining the ideal temperature levels in the pharmaceutical industry is essential for the production of drugs in laboratories, and their conservation, with the use of cold chains. For example, thermolabile drugs must be kept in the refrigerator at an average of 5 °C (between 2 and 8 °C). This is also the ideal range existing in Spain for the control of vaccines. Additionally, it is recommended that the temperature of the pharmacy premises remains below 30 °C.Temperature in products of the chemical industry
The measurement of temperature in the chemical industry is carried out in various stages of product manufacture. These can vary from the heat required to achieve reactions, to the sterilization of instruments or materials such as powders and oil-like substances using dry heat.
The aim of temperature control in the medical industry, as well as the pharmaceutical and chemical industries, has promoted the development of technologies that assist inspection. Indicator labels are functional devices that easily adhere to surfaces. There are reversible models, tools like thermometers for specific tasks, and also irreversible items that serve as temperature recorders, this is, they permanently alter. These elements change colour, as we can see when they reach a specific temperature.